Proposed Changes to Nebraska Recommendations for Manure Nitrogen Credit
April 7, 2020
Managing manure for economic and environmental benefit is based, in part, upon our ability to efficiently recycle manure nitrogen (N) between animals and crops.
Seeding Practices and Nitrogen Management for Western Nebraska Soybean: What Matters and Why
March 30, 2020
Continuous corn is the most common irrigated crop sequence in southwest Nebraska. Although rotating to other crops, such as soybeans, can mitigate some production issues of continuous corn and often boost the next year’s corn yield, larger adoption of soybeans has not readily occurred in this area.
New NebGuide - Crop Management to Reduce Soil Nitrous Oxide Emissions in Nebraska
February 24, 2020
A new NebGuide, G2322, authored by Bijesh Maharjan, Virginia Jin, Laila Puntel, Javed Iqbal, Tyler Williams, Humberto Blanco and Charles Wortmann, is available in both html and PDF formats.
Four Nebraska Farmers Share What They Learned From Conducting On-Farm Research Last Year
February 10, 2020
Conducting on-farm research can help provide the reliable answers you need to make decisions for your operation with confidence.
Manure Nitrogen Use for Increased Profit and Environmental Protection
February 5, 2020
Land application of manure and other organic materials supplies much N to Nebraska’s crop production. In contrast to most other nutrients applied in organic materials, the availability of manure-N and its fertilizer-N substitution value is not well-predicted.
$1.2 Million Grant to Help Corn and Wheat Growers Manage Nitrogen Fertilizer Application
January 13, 2020
Corn and wheat growers across Nebraska will be able to gain hands-on experience with cutting-edge technologies that will allow them to more precisely identify the amount of nitrogen fertilizer their crops need, while preventing excess nitrates from ending up in Nebraska’s water supply.
Agronomic Management for Reduced Nitrate Leaching
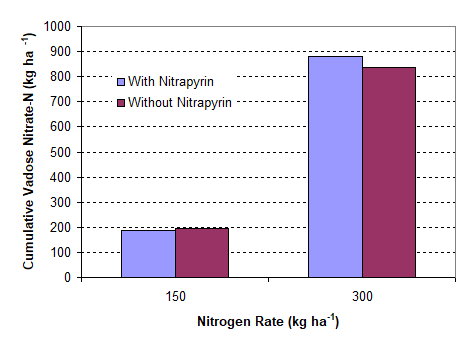
January 7, 2020
The leaching of nitrate to groundwater and the increasing occurrence of groundwater with excessive nitrate levels for human consumption is a major concern in Nebraska. The amount of leached NO3- depends on soil NO3- concentration at different soil depth layers and the quantity of water movement downward through these soil layers to beyond the root zone.
Soil Sampling for Better Fertilization Decisions
October 17, 2023
Recommendations for collecting soil samples to ensure the quality results needed for good management decisions about fertilizer, manure and lime application rates.