Corn Production

Nebraska Wheat Production
Nebraska ranks 17th in wheat production and is one of only five states in the U.S. where hard white wheat is grown. Wheat acreage is primarily located in the southern part of the Panhandle, southeast Nebraska and along the Nebraska-Kansas border. In 2023, Nebraska's wheat production resulted in $255 million from 880,000 acres harvested, according to USDA National Agricultural Statistics Service.
View UNL Variety Testing Program data on wheat via the link below.
Panhandle Contact:
Cody Creech
Dryland Cropping Systems Specialist
(308) 632-1266
ccreech2@unl.edu
Faculty Bio

Panhandle Contact:
Dipak Santra
Alternative Crops Specialist
(308) 632-1244
dsantra2@unl.edu
Faculty Bio

Wheat Production Resources
In-Season Resources
Like any crop, winter wheat should be grown as part of entire crop production system. Decisions made throughout the production system will impact the success of the winter wheat crop. Ecofarming is a popular production system for many winter wheat growers in Nebraska.
Crop Growth and Development
Understanding plant development can be helpful for making management decisions. The optimum timing of fertilizer, irrigation, herbicide, insecticide, and fungicide applications are best determined by crop growth stage rather than calendar date.
The impact of various crop stresses such as frost, heat, drought, disease, insect damage, or weed competition can be more accurately predicted with a clear understanding of the relationships between crop growth stage and plant response to stress.
Major Growth Stages:
- Germination
- Seedling
- Tillering
- Stem elongation (jointing)
- Booting
- Heading
- Flowering (anthesis)
- Milk
- Dough
- Ripening
Online Resources
- Ecofarming: Spring Row Crop Planting and Weed Control in Winter Wheat Stubble
Weed control, stubble management and planters for planting in winter wheat stubble. - Managing Corn and Sorghum Residues During the Pre-Winter Wheat Fallow Period
Maintain an appropriate residue cover with ecofarming to reduce soil erosion and conserve soil moisture. - Choosing the Right Tillage System for Row Crop Production
Systematically consider 19 criteria, in addition to the cost of conversion, in choosing a tillage system for your farming operation. - Relay Cropping Offers Economic Benefits - 2003 CropWatch Article
Relay cropping is a special version of double cropping, where the second crop is planted into the first crop before harvest, rather than waiting until after harvest as in true double-cropping. - Continuous Winter Wheat
- Estimating Winter Wheat Grain Yields (Nebraska Extension)
- Freeze Injury to Nebraska Wheat
- Wheat Kernel Damage (Source: Oklahoma State University)
- Plant Development--Growing Degree Days (Source: USDA)
- Tillering Patterns and Wheat Plant Stresses (Source: USDA)
Wheat Seeding Resources
Seedbed and Planting
A productive wheat crop starts with a firm, moist seedbed planted at the optimum time and at an adequate seeding rate.
- Seeding Rates for Winter Wheat in Nebraska
A review of winter wheat trials in Nebraska shows how widely the number of seeds per pound can vary within and among varieties, leading specialists to recommend a change to planting by seeds per acre rather than seeds per pound.
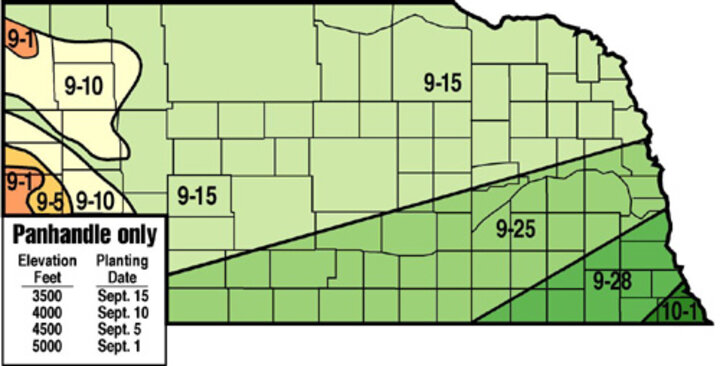
Seeding Dates for Nebraska
- Calibration of Sprayers (Also Seeders)
Provides methods and calculations for calibrating sprayers and seeders for accurate in-field application plus a section on converting weights and measures. - Management to Minimize and Reduce Soil Compaction
Understand how natural processes and management practices can reeduce existing soil compaction and minimize its further development.
Wheat Grazing Resources
Although grazing winter wheat is not as common in Nebraska as in the southern Great Plains, grazing can be used to lower risk from environmental stresses such as drought and hail, and economic risks associated with grain markets.
Growers can harvest wheat for grain only or they can harvest both the grain and forage. They can also harvest just the forage through “graze-out” of the crop.
*NOTE: To read or print PDF documents, you must have Adobe Reader installed on your computer. Download Adobe Reader Free
Variety Test Plots
View all wheat hybrid test results on the UNL Crop Variety and Hybrid Testing Program page