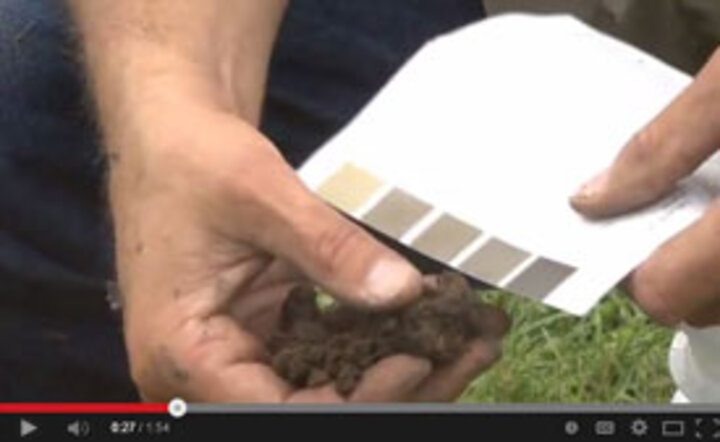
The quality of soil depends upon a variety of factors. NRCS has developed Soil Quality Kit Guides, fact sheets and materials for teachers to integrate into their soils curriculum. In addition, a curriculum has been developed to use in the classroom. These materials were created with funds provided by the Nebraska Environmental Trust. YouTube videos supplement these curricula as well.
In This Section:
- Components and Physical Properties of Soil
- Soil Organic Matter
- Using the Soil Textural Triangle
- Estimating Soil Moisture by Feel and Appearance
- Soil Quality Measurement
- Soil Bulk Density
- Soil Respiration
- Soil Electrical Conductivity
- Soil Web Survey
- Soil pH
- In Hand Soil Test Method
- Soil Nitrogen
- Soil Phosphorus
- Soil Infiltration
- The Scientific Method
- Soils Capstone Activity

Components and Physical Properties of Soil
Surface soil particles are held together, or "glued together," by various organic substances to create stable soil aggregates. These soil aggregates make it possible for air and water to move through the soil and during a rainstorm, are harder to wash away.
- Lesson Plan on the Physical Properties of Soil PDF | Powerpoint
- Lesson Plan on Soil Glue PDF
- Video: Soil Glue Demonstration
- Plant & Soil Sciences eLibrary: Physical Properties of Soil
Soil Organic Matter
Soil organic matter is the most important soil attribute you can manage to improve soil health. It consists of small plant residues and living organisms, decomposing organic matter and stable organic matter (humus), and serves as a reservoir for crop nutrients.
- Lesson Plan PDF | Powerpoint
- Videos: Overview | Test
- NRCS Guide: PDF
- Plant & Soil Sciences eLibrary: Soil Organic Matter
Using the Soil Textural Triangle
Soil texture plays a large role in crop production. Learn how to use a simple procedure to identify soil texture using a composite soil sample from the field and what differentiates a sandy or silt loam from a silty clay loam or silty clay and other soil types.
- Lesson Plan PDF | Texture by Feel Key
- Video: Texture by Feel Procedure
- Plant & Soil Sciences eLibrary: Soil Texture
Estimating Soil Moisture by Feel and Appearance
Learn this in-field procedure for determining available soil moisture by the look and feel for various soil types common to Nebraska and the importance of knowing soil moisture to irrigation water management.
- Lesson Plan PDF | Powerpoint | NRCS Guide
- Video: Estimating Soil Moisture
- Related Resource: UNL NebGuide
- Plant & Soil Sciences eLibrary: Soil Water
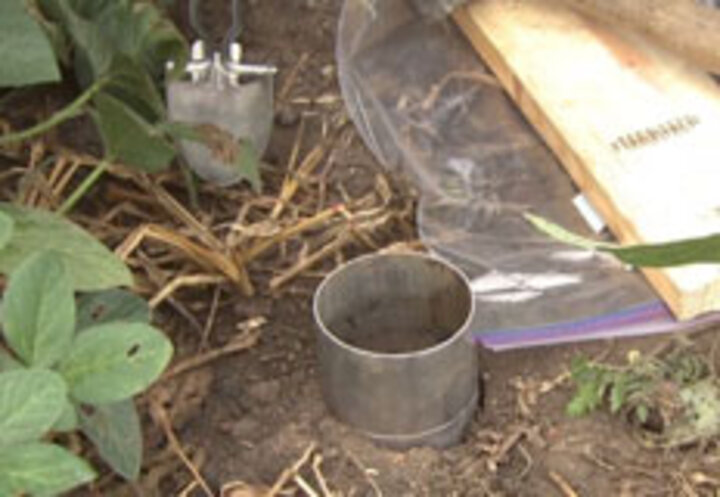
Soil Quality Measurement
Soil quality integrates the physical, chemical, and biological components of soil and their interactions. These resources examine field site or characterization and soil sampling guidelines.
- Lesson Plan PDF | Powerpoint
- Videos: Soil Sampling & Soil Quality Measurement
- NRCS Guide: PDF | Soil Quality Test Bucket Checklist
- Plant & Soil Sciences eLibrary: Fundamentals of Soil Testing
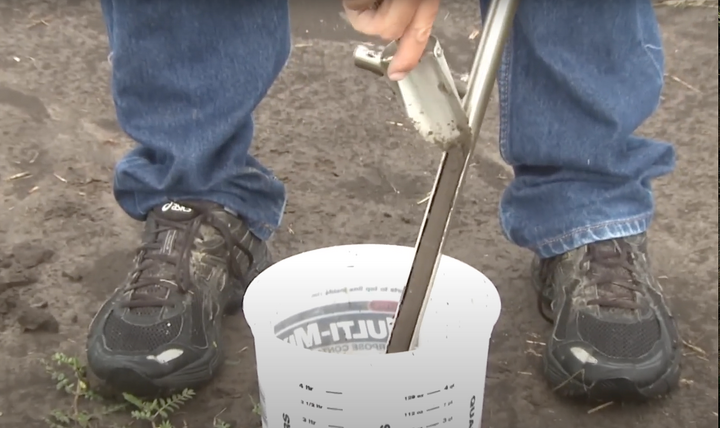
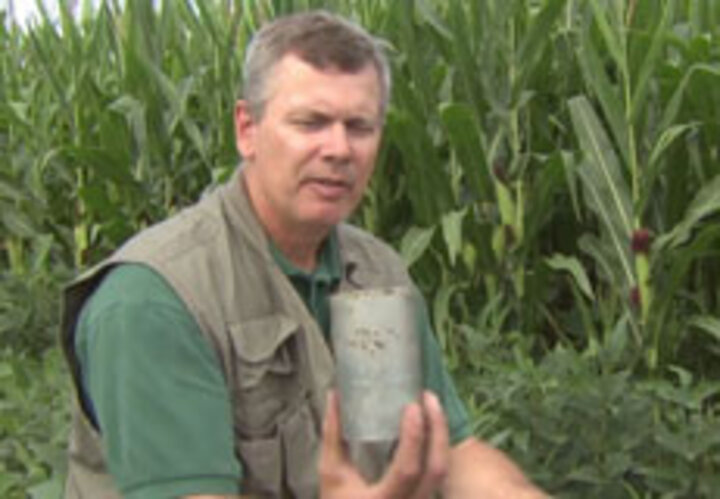
Soil Bulk Density
Bulk density is an indicator of soil compaction and soil health. It affects infiltration, rooting depth, plant nutrient availability, and soil microorganism activity. Understanding and measuring this soil attribute can guide soil management practices. These resources cover factors affecting the bulk density, soil moisture, and soil density problems.
- Lesson Plan: PDF | Powerpoint
- Videos: Overview | Test
- NRCS Guide: PDF
- Plant & Soil Sciences eLibrary
Soil Respiration
Soil respiration is a measure of carbon dioxide (CO2) released from the soil when soil organic matter decomposes and when plant roots and soil fauna respire. It is a sign of soil biological activity and an important indicator of soil health.
- Lesson Plan: PDF | Powerpoint
- Videos: Overview | Test
- NRCS Guide: PDF
Soil Electrical Conductivity
Soil electrical conductivity (EC) is a measure of soil salinity and an important indicator of soil health. Excess salts can hinder plant growth, nutrient availability, and other soil processes and affect soil-water balance.
- Lesson Plan: PDF | Powerpoint
- Videos:
- NRCS Guide: PDF
Soil Web Survey
Lesson Plan: PDF
Soil pH
Soil pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a soil. Consider factors that affect soil pH, soil pH management options, the relationship of pH to soil function and measure the pH in soil.
In Hand Soil Test Method - Nitrogen, Phosphorus, pH
Soil Nitrogen
Nitrogen is the most abundant element in the atmosphere and is usually the most limiting crop nutrient. Investigate factors that affect soil nitrogen, nitrogen management, and measure soil nitrate/nitrite.
- Lesson Plan: PDF | Powerpoint
- Videos: Overview | Testing
- NRCS Guide: PDF
Soil Phosphorus
Phosphorus' primary role in a plant is to store and transfer energy produced by photosynthesis for use in growth and reproductive processes. Analyze phosphorus management practices and test soil phosphate.
- Lesson Plan: PDF | Powerpoint
- Videos: Overview | Test
- NRCS Guide: PDF
- Plant & Soil Sciences eLibrary: Phosphorus and Potassium in the Soil
Soil Infiltration
Infiltration refers to the soil's ability to allow water movement into and through the soil profile. Check into management practices that impact infiltration, problems related to infiltration and measure infiltration in soil.
- Lesson Plan: PDF | Powerpoint
- Videos: Overview | Test
- NRCS Guide: PDF
The Scientific Method
Lesson Plan: PDF