Dicot Weeds
Dicot (broadleaf) weed identification, just like monocot identification, can be challenging. The base plant identification parts are similar between monocots and dicots; however, there are additional characteristics that are critical in proper dicot (broadleaf) weed identification.
Leaf Arrangement (Figure 1)
- Alternate leaf arrangement is characterized by a single leaf per node.
- Opposite leaf arrangement is characterized by two and only two leaves at a node on opposing sides of the stem.
- Whorled leaf arrangement is characterized by three or more leaves per node are arranged in a circular pattern.

Leaf Type (Figure 2):
- Simple — a leaf that is undivided, meaning it has only one definite segment present between the stem and the end of the blade.
- Compound leaves are divided into definite and distinct segments called leaflets.
- Pinnately leaflets are arranged on opposite sides of the leaf axis, similar to a feather.
- Palmately leaflets radiate from a central point, like fingers radiating from the palm of a hand.

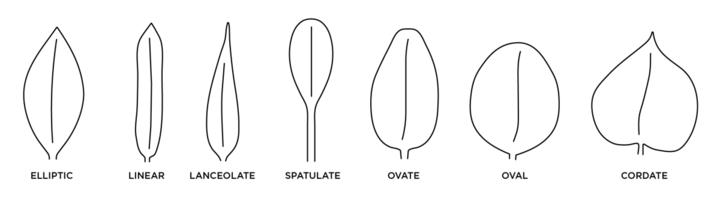
Leaf Shape (Figure 3):
- Elliptic leaves are broadest in the middle and narrower at either end.
- Linear leaves are long and narrow with the sides being close to parallel to each other.
- Lanceolate leaves are much longer than wide, with the widest point below the middle of the leaf.
- Spatulate leaves look like a spatula, with the tip being rounded and gradually tapering to the base.
- Ovate leaves are egg-shaped, lacking a pointed tip.
- Oval leaves are round to oval, lacking a pointed tip.
- Cordate leaves are heart-shaped.
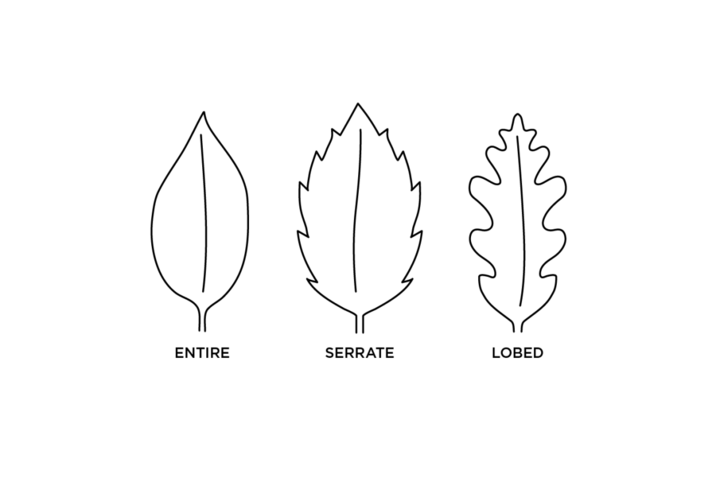
Leaf Margin (Figure 4):
- Smooth — the entire margins are smooth and do not have any teeth, notches or divisions.
- Dentate or Serrate leaves have toothed or saw-like margin.
- Lobed leaves have indentations along the margin that cut inward toward the leaf midvein.
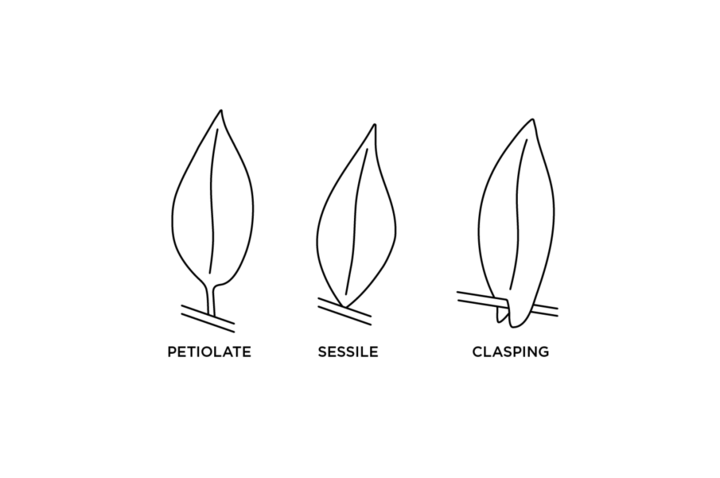
Leaf Attachment (Figure 5):
- Petiolate leaves have a stalk (petiole) that attaches them to the stem.
- Sessile leaves do not have a petiole and are attached directly to the stem.
- Clasping leave are sessile and have a base that wholly or partly wraps around the stem.
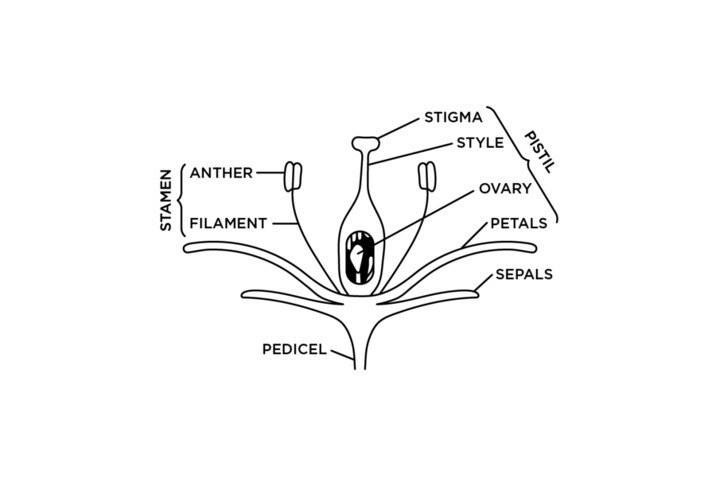
Flower Parts (Figure 6):
- Sepals — outermost whole of leaf-like structures that protect the bud. Typically small and green in color, but may be just as colorful as the petals.
- Calyx — the collection of sepals.
- Petals — the next whorl of leaf-like structures. They are usually colorful and attractive.
- Corolla — the collection of petals.
- Tepals — petal-like structures which are found on some plants that do not have petals and sepals but just one undifferentiated whorl.
- Stamen — male reproductive organ consisting of an anther and filament.
- Anther — bears pollen.
- Filament — thread-like structure that supports that anther.
- Pistil — female reproductive organ consisting of the stigma, style and ovary.
- Stigma — the tip of the pistil and receives pollen.
- Style — the narrowed portion that connects the stigma to the ovary.
- Pedicel — the stalk that attaches the flower to the stem.
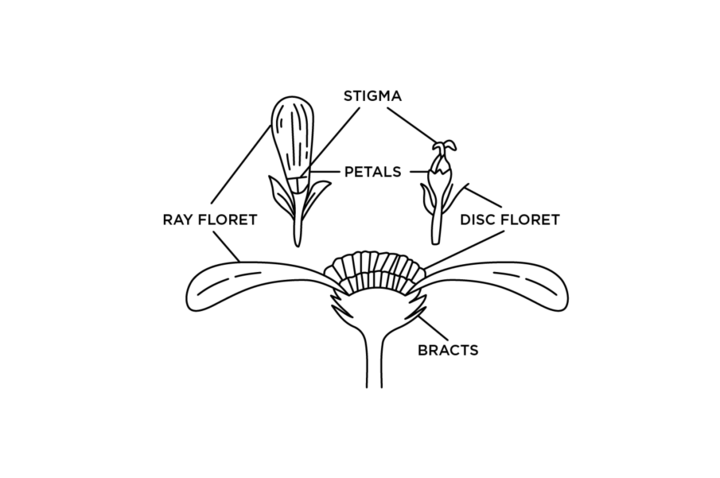
Asteraceae Family Unique Features (Figure 7):
- Florets
- Ray
- Disc
- Bracts — leaf- or scale-like structures that surround the base of the flower.
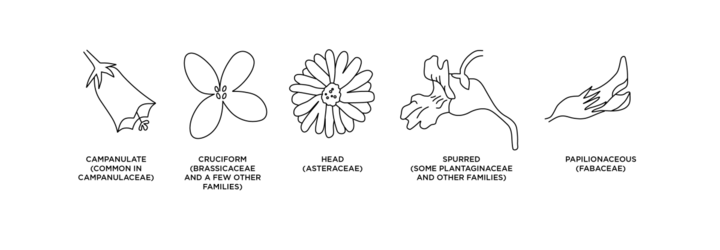
Flower Shape (Figure 8):
- Campanulate — bell-shaped flower with a wide tube and flared lobes (petal tips).
- Cruciform — cross-shaped flower with four petals at right angles to one another.
- Head
- Spurred
- Papilionaceous — pea-shaped flower that have a large upper petal called the standard, two large side petals called wings and two lower petals often fused together called the keel, which encloses the stamens and stigma.
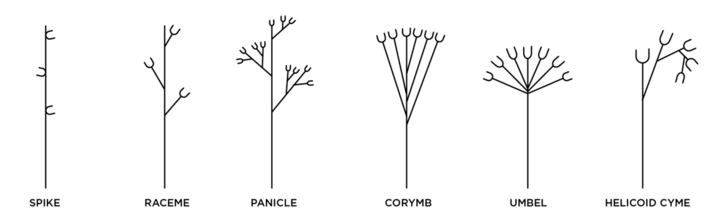
Inflorescence Types (Figure 9):
- Spike — the flower is attached directly to the stem and pedicles (stalks) are absent.
- Raceme — pedicels attach the flowers to the stem.
- Panicle — compound or branched racemes.
- Corymb — pedicles are different lengths with the pedicels at the base are longer than those near the top, giving a flat to rounded top.
- Umbel — a flat topped or convex inflorescence with the pedicels arising from a common point, like an umbrella.
- Helicoid cyme — coiled like a scorpion’s tail.
DID YOU KNOW?
There are multiple online sources to aid in weed identification, such as University of Missouri Weed ID Guide, which is also available as a downloadable app.

Nebraska Soybean Board graciously provided the funding for the Soybean Management Guide.
Course authored by:
Amy Timmerman, extension educator; Aaron Nygren, extension educator; Brandy VanDeWalle, extension educator; Loren Giesler, Plant Pathologist Department head; Ron Seymour, extension educator; Keith Glewen, former extension educator; Charles Shapiro, emeritus extension soil scientist; Amit Jhala, extension weed specialist; Don Treptow, former graduate student
