A research project is underway at the Eastern Nebraska Research and Extension Center (ENREC) near Mead to evaluate a double crop production system. The experiment was designed by University of Nebraska faculty and graduate students as a potential alternative to the traditional corn/soybean rotation commonly used in the area.
A corn/soybean rotation can often lead to soil degradation, over-reliance on pesticides and fertilizers, frequent outbreaks of diseases and insects, herbicide-resistant weeds, and increased financial risks associated with low market prices. Diversifying a crop production system by including additional crops or methods can help overcome many of these issues.
This experiment used yellow field peas as the first crop in the double crop system. Yellow field peas are typically planted in March and harvested in July. Although not evaluated in this experiment, winter wheat (seeded in September/October and harvested in July) could be another cool-season crop option and provide additional benefits by overwintering and protecting the soil. Wheat has the ability to perform well in eastern Nebraska. (See variety trial results and related article.)
The objectives of this project are:
- to evaluate the yield potential of pulse crops (field peas, lentils, and chickpeas) in eastern Nebraska. Current market prices for pulse crops are on this USDA site.
- to evaluate the feasibility of double cropping yellow field peas with short-season crops (corn, soybean, grain sorghum, millet and sunflower) and annual forages (forage sorghum and sorghum-Sudangrass) by measuring crop production and performing an economic analysis.
- to investigate the benefits of incorporating cover crops and livestock grazing into the cropping systems.
- to design the cropping system with an extended growing season that will minimize pesticide and fertilizer inputs and be more water-use efficient.
Pulse Crops Variety Trial
Although the double crop experiment is ongoing, an important component was to conduct a pulse crop variety trial to identify which varieties are best adapted to the environment in eastern Nebraska (Figure 1). The variety trial (Figure 2) was conducted adjacent to the double crop experiment at ENREC. Yellow peas, green peas, lentils, and chickpeas were planted early in the spring and evaluated for their characteristics such as flowering, maturity, plant height, test weight and yield (Table 1).
Short season crops (corn, soybean, sunflower, millet and milo), annual forages (forage sorghum and sudangrass) and cover crops were planted right after field pea harvest. The research is ongoing and data on yield and water use will be shared following harvest.
This research is being funded by the North Central SARE and the pulse crop seed industry including Meridian Seed, Pulse USA, Great Northern Ag, Arrow Seed, Montana Integrity, and NS Seed.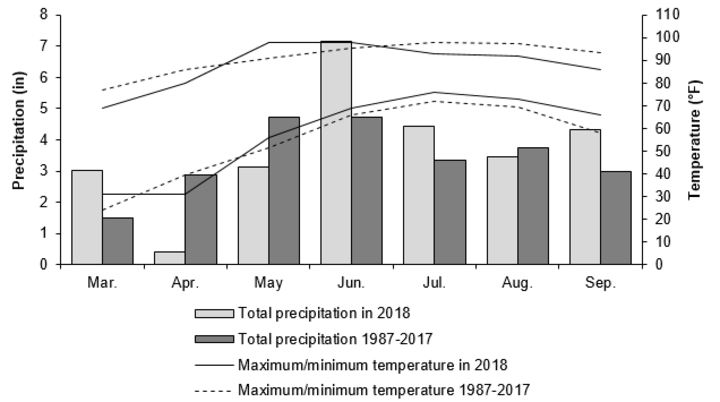
Trial Summary
- Location: Mead, Nebr. - Saunders County (GPS: 41°10'57.8"N 96°27'57.8"W)
- Weather info: see Figure 1
- Soil type: Silt Loam and Silt Clay Loam
- Tillage practice: no-till
- Previous crop: corn
- Seeding (date, rate, depth, inoculant):
— Yellow peas (04/05/2018, 310,000 live plants/acre, 1.5-2 inches deep, liquid and peat inoculant at a 2x rate)
— Green peas (03/30/2018, 310,000 live plants/acre, 1-1.5 inches deep, two different peat-based pea inoculants)
— Lentils (03/30/2018, 310,000 live plants/acre, 1 inch deep, two different peat-based pea inoculants)
— Chickpeas (04/12/2018, 300,000 for Orion and 220,00 live plants/acre for Frontier, 1.5 inch deep, diluted liquid inoculant plus a full rate of Verdesian N-Dure peat inoculant) - Herbicide program: Sharpen 2 oz + Prowl 2 pt
- Harvest (date): yellow and green peas (07/12/2018); lentils (07/20/2018); chickpeas (08/13/2018)

| Variety | Brand | 50% bloom (DAP)* | Flowering rating | Matur (1-10)* | Plant height (in) | harvest Moist. (%) | Test wt (lbs/bu) | Yield (bu/ac)* | Yield (lb/ac) | Yield rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yellow Peas | ||||||||||
| Agassiz | Meridian Seed | 58 | Early | 8 | 20.1 | 13.7 | 62.9 | 48 | 2893 | 1 |
| AAC Profit | Great Northern Ag | 60 | Late | 6 | 27.6 | 23.2 | 60.8 | 45 | 2696 | 2 |
| Jetset | Meridian Seed | 58 | Early | 10 | 24 | 12.7 | 63.7 | 44 | 2637 | 3 |
| AC Earlystar | Meridian Seed | 58 | Early | 8 | 24.3 | 14.1 | 59.7 | 42 | 2516 | 4 |
| CDC Inca | Meridian Seed | 60 | Late | 6 | 21.3 | 15.8 | 62.8 | 42 | 2493 | 5 |
| Hyline | Great Northern Ag | 59 | Mid | 7 | 24.9 | 19.3 | 60.4 | 41 | 2468 | 6 |
| AAC Carver | Meridian Seed | 58 | Mid | 7 | 27.6 | 14.8 | 62 | 41 | 2459 | 7 |
| Spider | Great Northern Ag | 59 | Mid | 7 | 24.9 | 15.1 | 62.8 | 41 | 2452 | 8 |
| CDC Saffron | Meridian Seed | 59 | Mid | 8 | 23.7 | 15.5 | 63.9 | 41 | 2445 | 9 |
| 4193 | Montech | 57 | Early | 8 | 21 | 13.3 | 62.4 | 38 | 2303 | 10 |
| SW Midas | Pulse USA | 58 | Mid | 9 | 19.2 | 13.2 | 62.8 | 37 | 2231 | 11 |
| LG Sunrise | Pulse USA | 57 | Early | 4 | 27.6 | 19.9 | 59.5 | 37 | 2210 | 12 |
| 1057 | Montana Integrity | 60 | Late | 8 | 29.4 | 13.7 | 64 | 37 | 2207 | 13 |
| 4152 | Montech | 58 | Mid | 7 | 23.7 | 15.5 | 62.3 | 36 | 2181 | 14 |
| DS-Admiral | Pulse USA | 57 | Early | 10 | 21.6 | 12.7 | 62.7 | 36 | 2137 | 15 |
| CDC Amarillo | Meridian Seed | 60 | Late | 5 | 27.6 | 22.7 | 59.4 | 36 | 2135 | 16 |
| Nette 2010 | Pulse USA | 57 | Early | 10 | 18.9 | 12.2 | 62.6 | 36 | 2133 | 17 |
| CDC Spectrum | Meridian Seed | 60 | Late | 3 | 29.4 | 24.8 | 58.7 | 35 | 2084 | 18 |
| Bridger | Great Northern Ag | 57 | Early | 8 | 23.1 | 14.6 | 63 | 35 | 2084 | 19 |
| Navarro | Great Northern Ag | 56 | Early | 6 | 25.5 | 14.8 | 62.3 | 34 | 2063 | 20 |
| Salamanca | Great Northern Ag | 59 | Mid | 7 | 29.4 | 15.9 | 62.4 | 34 | 2027 | 21 |
| LG Amigo | Pulse USA | 58 | Mid | 5 | 26.1 | 16.4 | 62.1 | 33 | 2001 | 22 |
| Partner | NS Seed | 58 | Mid | 8 | 22.8 | 14.2 | 48.7 | 28 | 1693 | 23 |
| Durwood | Pulse USA | 58 | Mid | 6 | 30.9 | 16.6 | 61.7 | 26 | 1555 | 24 |
| Dukat | NS Seed | 56 | Early | 10 | 12.3 | 13.5 | 62.8 | 22 | 1318 | 25 |
| Average of all Varieties | 58 | Mid | 7 | 24.3 | 15.9 | 61.4 | 37 | 2217 | ||
| Difference required for significance at 5% | 3 | 4 | 5 | 8 | 12 | 716 | ||||
| Green Peas | ||||||||||
| CDC Striker | Pulse USA | 9 | 25.8 | 13.6 | 63.7 | 46 | 2740 | 1 | ||
| Shamrock | Great Northern Ag | 10 | 17.7 | 13.4 | 62.4 | 44 | 2665 | 2 | ||
| SW Arcadia | Pulse USA | 10 | 21.3 | 12.1 | 63.7 | 43 | 2556 | 3 | ||
| CDC Greenwater | Meridian Seed | 9 | 27.6 | 13 | 63.4 | 41 | 2471 | 4 | ||
| AAC Comfort | Meridian Seed | 3 | 30.3 | 26.2 | 58.1 | 39 | 2319 | 5 | ||
| Empire | Great Northern Ag | 4 | 35.7 | 17.6 | 62.7 | 29 | 1761 | 6 | ||
| Junior pea | NS Seed | 6 | 26.1 | 18.2 | — | 27 | 1650 | 7 | ||
| Average of all Varieties | 7 | 26.4 | 16.3 | 62.3 | 38 | 2309 | ||||
| Difference required for significance at 5% |
2 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 10 | 648 | ||||
| Lentils | ||||||||||
| CDC Maxim CL | Pulse USA | 10 | — | 31 | 1835 | 1 | ||||
| CDC Invincible CL | Pulse USA | 10 | — | 29 | 1738 | 2 | ||||
| Chickpeas | ||||||||||
| CDC Orion | Meridian Seed | 12.2 | 53.9 | 40 | 2418 | 1 | ||||
| CDC Frontier | Meridian Seed | 12.7 | 55.4 | 35 | 2088 | 2 | ||||
| * DAP, Days after planting * 1 = late maturing, 10 = early maturing * Yield at 60 lbs/bu and 13% moisture | ||||||||||

