This is the third article of CropWatch's digital agriculture series (DA), “How Digital is Agriculture in Nebraska?” See the links below for more.
Articles in this Series:
Part 3: Barriers to Adoption of Digital Agriculture in Nebraska
Part 4: Top Five Digital Agriculture Technologies Used in Nebraska
Part 5: DAWN Dashboard: A Decision Support Tool for the Corn Belt
This CropWatch article is part of the digital agriculture series (DA), “How Digital is Agriculture in Nebraska?” If you missed our first articles, you can check them on the links provided at the end of this article.
The Digital Farming Lab, led by Dr. Guillermo Balboa, conducted a statewide survey to assess the status of DA in Nebraska. For more resources about DA in Nebraska, visit our UNL Digital Agriculture website, which aims to centralize all UNL efforts in teaching, research and extension on digital afgriculture.
We want to start by refreshing the concept of digital agriculture. Digital agriculture (DA) can be defined as the use of new technologies, combining multiple data sources and advanced analytical methods, and integrating systems that allow farmers and stakeholders of the agricultural value chain to improve the food production system. Digital agriculture includes the Internet of Things (IoT), precision agriculture, blockchain, big data, digital platforms and artificial intelligence.
The first article in the series introduced the survey, defined digital agriculture and how farmers perceive it, and summarized 10 facts about DA in Nebraska (10 facts flyer). Our second article highlighted the level of adoption of 33 different technologies in the state of Nebraska. This third article presents the barriers identified for the adoption of DA tools.
Farmers were asked about different levels of barriers to the adoption of digital agriculture. They categorized them as no barriers, moderate barriers, high barriers or just not sure category (Figure 1). The ranking combining high and moderate barriers is:
- Lack of information about digital agriculture value: 75%
- Lack of qualified labor to manage digital agriculture: 65%
- Lack of time: 63%
- Overwhelming number of technologies: 60%
- Number of service providers: 58%
- Technology cost: 56%
- Available training: 53%
- Not enough field days 44%
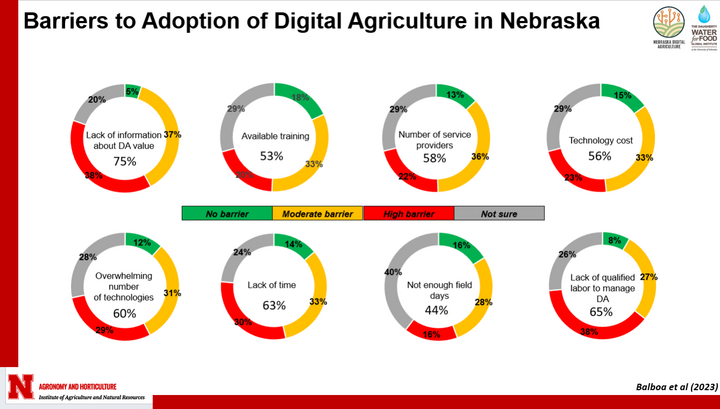
The lack of information about DA value was rated as the highest barrier category. This was followed by a lack of qualified labor to manage DA technologies and a lack of time (63%). The barrier of not having enough field days to be in contact with technology was the only barrier, with less than 50%. Technology cost, historically associated as a main barrier to adopting DA, ranked six out of eight.
A recent literature review (Dibbern et al., 2024) shows that barriers to the adoption of DA include farmers' economic constraints, lack of infrastructure and technological knowledge, the perceived usefulness of technology, willingness to innovate and risk-taking. Academic training was included in this review as a barrier to adoption.
The barriers identified to the adoption of digital agriculture in Nebraska provided critical input for the University of Nebraska's current research and extension efforts.
Stay tuned for our fourth article in the series, briefly describing the top five DA tools most used in Nebraska and their benefits associated.
This research was supported by the Precision Nitrogen Conservation Innovation Grant (CIG — USDA NR203A750013G014). The survey was conducted in cooperation with the UNL Bureau of Sociological Research.
References
Balboa, G. R., Puntel, L. A., & Thompson, L. (2023) On-Farm Research Network Ecosystem Increased Awareness and Use of Digital Agriculture in Nebraska [Abstract]. ASA, CSSA, SSSA International Annual Meeting, St. Louis, MO. https://scisoc.confex.com/scisoc/2023am/meetingapp.cgi/Paper/150933
Puntel, L. A., Bolfe, É. L., Melchiori, R. J. M., Ortega, R., Tiscornia, G., Roel, A., Scaramuzza, F., Best, S., Berger, A. G., Hansel, D. S. S., Palacios Durán, D., & Balboa, G. R. (2022). How digital is agriculture in a subset of countries from South America? Adoption and limitations. Crop and Pasture Science, 74, 555–572. https://doi.org/10.1071/CP21759
Dibbern, T., Romani, L.A.S., Massruhá, S.M.F.S., 2024. Main drivers and barriers to the adoption of Digital Agriculture technologies. Smart Agric. Technol. 8, 100459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atech.2024.100459

