Grain-type field peas are a cool season grain crop (typically planted in mid-March and harvested late-July) grown as an alternative for no-till summer fallow in a semiarid cereal-based cropping systems such as wheat-corn-fallow and/or wheat-fallow (Figure 1). Previously, no information was available on how field pea responds to seeding practices in semiarid Nebraska as compared to other major field pea growing regions (Table 1). The objective of this study was to determine the economically optimal seeding rate, seeding depth, and inoculant use to grow field peas in western Nebraska.
Also see:
Field Pea Rotational Costs and Benefits
| Region | Seeding Depth (inch) |
Seeding Date | Seeding Rate (lbs/ac)* |
Source |
| Manitoba, CA | 1 - 2 | Before May 21 | 150-171 | Manitoba Agriculture (2016) |
| Alberta, CA | 1 - 2 | Before May 15 | 161-193 | Alberta Pulse Growers (2016) |
| Saskatchewan, CA | 1– 3 | Mid-April to Mid-May | 161-184 | Saskatchewan Pulse Growers (2016) |
| North Dakota, USA | 1 - 3 | Early April to Mid-May | 161-184 | Schatz and Enders (2009) |
| Montana, USA | 1 - 3 | Late March to early May | 184-229 | McVay et al. (2016) |
| South Dakota, USA | 1.5 - 3 | Mid-April | 184 | Beck et al. (2015) |
| Washington/Idaho, USA | 1.5 - 3 | March 25 - May 10 | 191-231 | Muehlbauer et al. (1997) |
| Wisconsin/Minnesota, USA | 1 - 3 | Mid-March to Mid-April | 204 | Oelke et al. (1991) |
| *Seeding rates target final plant population ranging from 300,000 to 500,000 plants/ac | ||||


Seeding Rate Studies
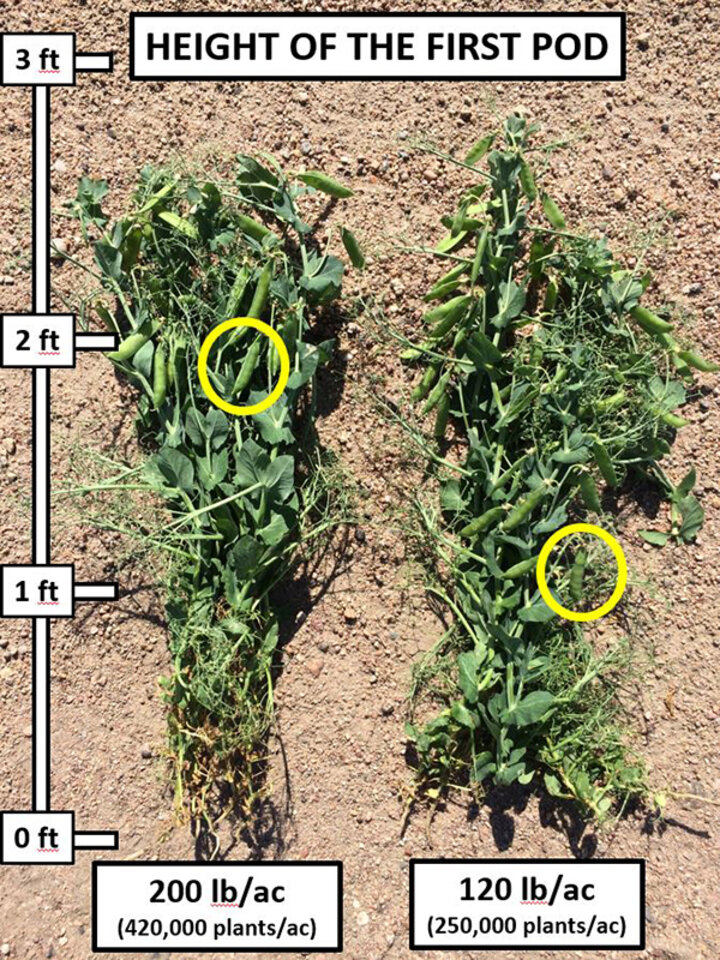
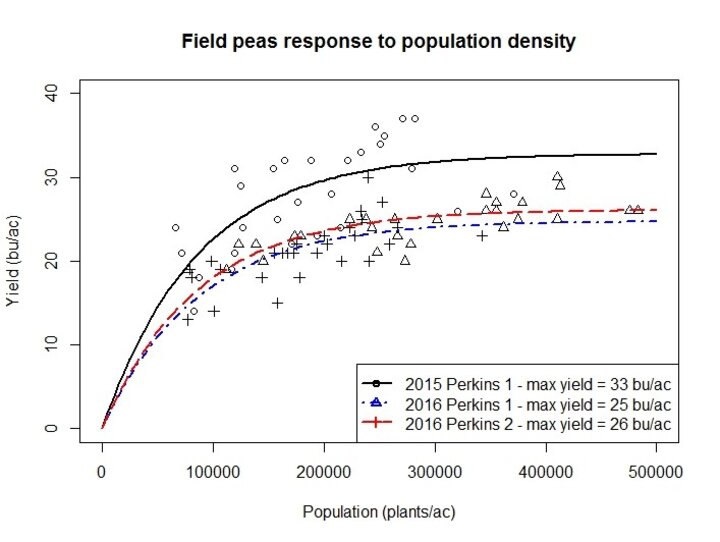
Results from our three site-year study on seeding rates conducted in 2015 and 2016 in Perkins County showed the field pea response to plant population was linear at lower densities (up to 200,000 plants/ac), then began to plateau at about 200,000 plants/ac, reaching its maximum at approximately 310,000 plants/ac (Figure 2). Yield in 2015 was higher (maximum yield 33 bu/ac) than in 2016 (maximum yield 25-26 bu/ac) regardless of population density. We have also observed that field peas planted at lower population densities are maturing later, are able to produce more pods per plant, and set first harvestable pod at lower plant heights (Figure 4).
Although yield response at populations higher than 310,000 plants/ac was seldom observed, there is an indication that for yield goals greater than 30 bu/ac increasing seeding rate may be justified. Higher yield goals for field pea may be obtained under irrigation or in years when hot ambient temperatures do not occur during flowering when the plant is most sensitive to heat/drought stress.
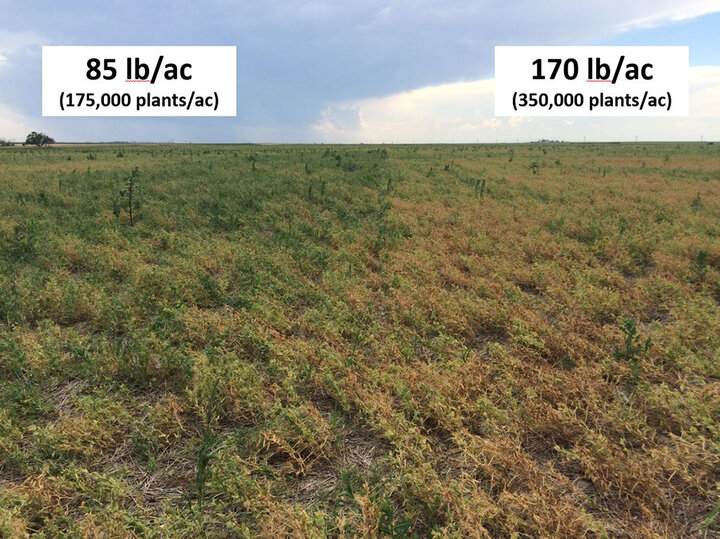
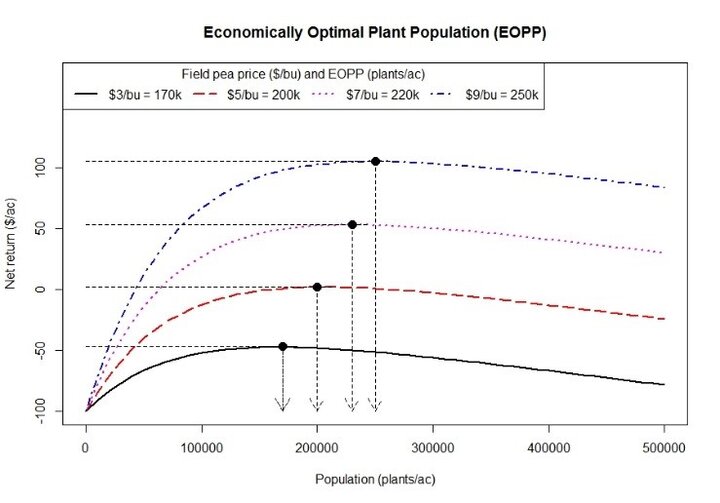
The economically optimal plant population (EOPP) can be defined as the population that maximizes profit made on investment, which in this case is seed. Our results suggest that maximum profit is obtained at 220,000 plants/ac, which corresponds to a seeding rate of 116 lb of seed/ac (Figure 3). A penalty of about $0.19/ac may occur for each additional pound of seed planted over this EOPP. Planting higher populations to maximize yield potential is not always the best economic strategy due to the asymptotic nature of yield response to planting density.
Further research is needed to validate our optimal seeding rates for Nebraska (116 lbs/ac) as recommendations for seeding rates in other field pea growing regions range from 150 to 230 lbs/ac (Table 1).
Seeding Rate Recommendation
Although this study shows the potential for reduction in field pea population without lowering profits, these results are yet to be confirmed in additional production years and/or locations and should be considered cautiously until further research is completed and results validated. Current recommendations for field pea seeding rates range from 180 to 200 lb/ac (Figure 5). Further research to evaluate optimal seeding rates will be conducted across a broader geographic region in 2017 and 2018.
Seeding Depth and Rhizobia Inoculant Studies
Seeding Depth Study
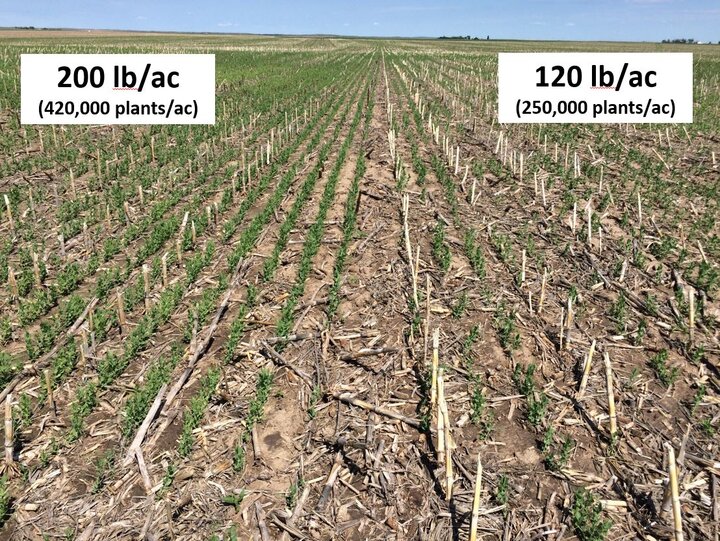
Field pea has relatively large seeds and generally requires deeper seeding than smaller seeded cereals for proper soil-seed contact (Figure 6; Table 1). Large seeds can emerge from greater depths because they have more stored energy. However, to ensure proper germination and emergence, seeds should be placed in soil with adequate moisture. For example, dry top soil moisture at planting is the main reason why slightly deeper seeding depth is recommended for the warm dry climate of the Pacific Northwest (1.5 inches) as compared to Canada and the northern Great Plains (1 inch; Table 1).
Although field peas can tolerate deeper seeding, research from Canada showed that seeding depth greater than 2.5 inches can cause significant reduction in stand and up to 8.5% yield loss as compared to shallower seeding (1-2.5 inches).



Rhizobia Inoculant Study
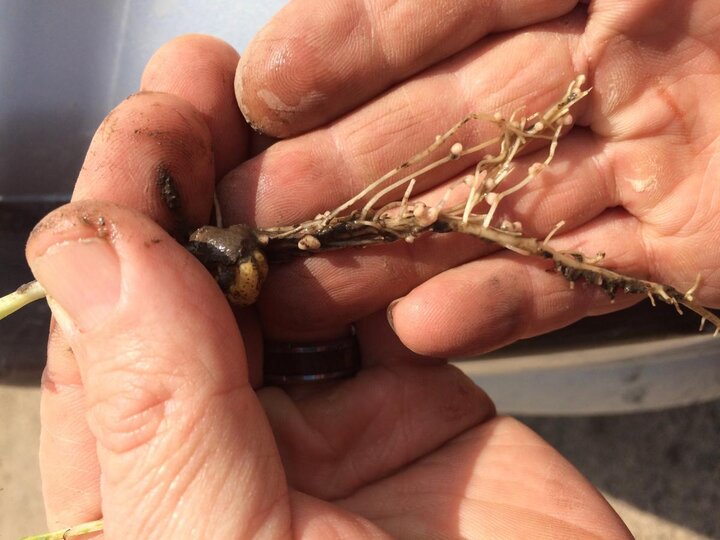
The need to re-introduce rhizobia with each field pea crop depends on many factors, the most crucial being the bacteria’s ability to survive in the soil over a given time. Research in Mediterranean soils showed that population size of field pea rhizobia is likely to be under the optimal nodulation thresholds (
Preliminary seeding depth and rhizobia inoculant studies (Figure 6) were conducted in 2015 (Site 1). In 2016, the potential for carryover of rhizobia inoculant in the soil was also tested at Site 2 where field pea had been grown two years earlier in 2014 and Site 3 where field pea had been grown three years earlier in 2013.
Seeding Depth and Inoculant Recommendation
We observed no significant difference in yield between three seeding depths (Table 2). We recommend placing the seeds 1 to 3 inches deep where there is moisture and good seed-to-soil contact can be obtained.
Although yield differences between inoculated and non-inoculated field pea were not observed, non-inoculated field peas did not produce nodules and had to rely solely on residual soil nitrogen rather than biological fixation. Therefore, we recommend using inoculant at planting until more research is conducted to evaluate field pea nitrogen uptake and inoculation needs.
| Study | Year | Location | Treatment | Yield (bu/ac) |
| Seeding Depth (inches) | 2015 | Site 1 | 1.5 | 29 |
| 2.5 | 26 | |||
| 2016 | Site 2 | 1 | 10 | |
| 2 | 13 | |||
| 3 | 12 | |||
| 2016 | Site 3 | 1 | 22 | |
| 2 | 23 | |||
| 3 | 25 | |||
| Rhizobia Inoculant | 2016 | Site 2 | None | 10 |
| Liquid Inoculant | 13 | |||
| 2016 | Site 3 | None | 20 | |
| Liquid Inoculant | 23 |

