This resource was originally published by the Nebraska Water Center, part of the Daugherty Water for Food Institute at the University of Nebraska.
Nitrogen is an essential plant nutrient but increasingly found in our water. The following is a brief history about nitrogen in Nebraska.
For a list of references, visit UNL Water.
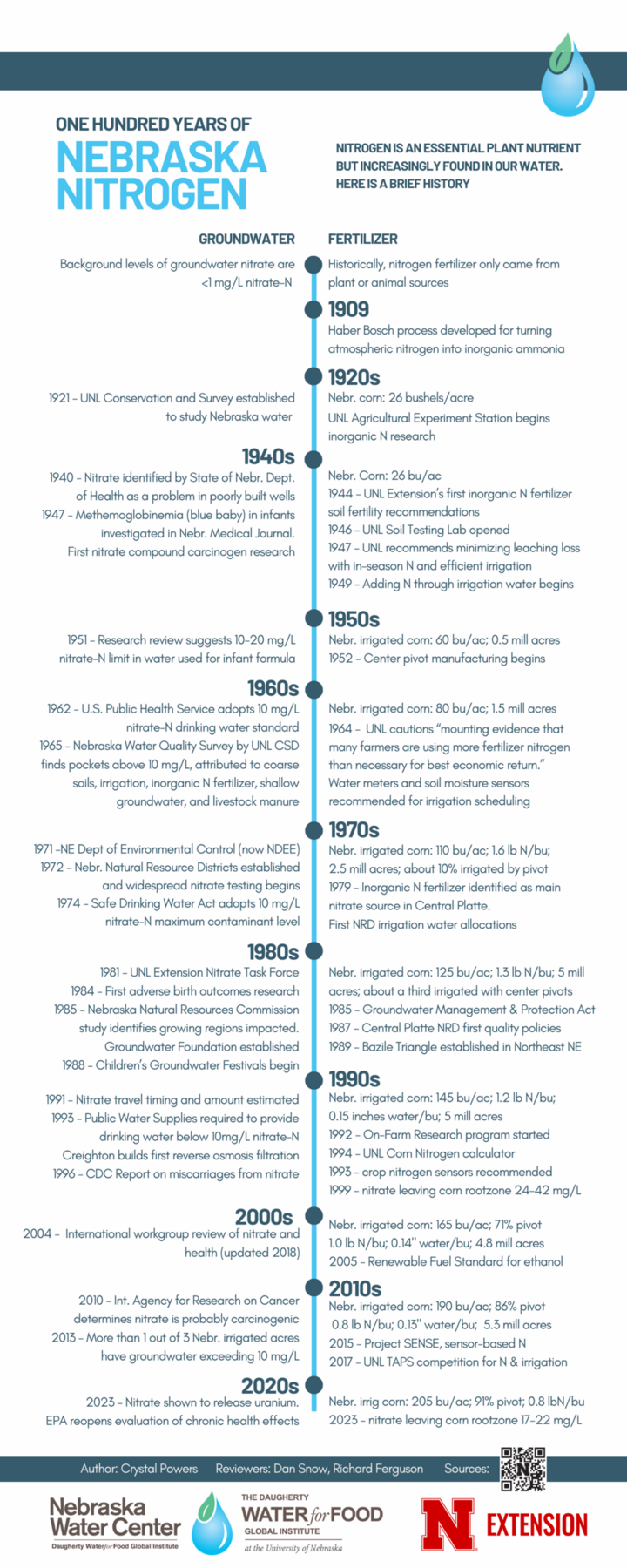
| Groundwater | Fertilizer | |
|---|---|---|
| Background levels of groundwater nitrate are | Historically, nitrogen fertilizer only came from plant or animal sources. | |
| 1909 | Haber Bosch process developed for turning atmospheric nitrogen into inorganic ammonia. | |
| 1921 — UNL Conservation and Survey established to study Nebraska water. | 1920s | Nebraska corn: 26 bushels/acre UNL Agricultural Experiment Station begins inorganic N research. |
| 1940 — Nitrate identified by State of Nebraska Department of Health as a problem in poorly built wells. 1947 — Methemoglobinemia (blue baby) in infants investigated in Nebraska Medical Journal. First nitrate compound carcinogen research. | 1940s | Nebraska corn: 26 bu/ac 1944 — UNL Extension’s first inorganic N fertilizer soil fertility recommendations. 1946 — UNL Soil Testing Lab opened. 1947 — UNL recommends minimizing leaching loss with in-season N and efficient irrigation. 1949 — Adding N through irrigation water begins. |
| 1951 — Research review suggests 10-20 mg/L nitrate-N limit in water used for infant formula. | 1950s | Nebraska irrigated corn: 60 bu/ac; 0.5 million acres 1952 — Center pivot manufacturing begins. |
| 1962 — U.S. Public Health Service adopts 10 mg/L nitrate-N drinking water standard. 1965 — Nebraska Water Quality Survey by UNL CSD finds pockets above 10 mg/L, attributed to coarse soils, irrigation, inorganic N fertilizer, shallow groundwater, and livestock manure. | 1960s | Nebraska irrigated corn: 80 bu/ac; 1.5 million acres 1964 — UNL cautions “mounting evidence that many farmers are using more fertilizer nitrogen than necessary for best economic return.” Water meters and soil moisture sensors recommended for irrigation scheduling. |
| 1971 — Nebraska Department of Environmental Control (now NDEE). 1972 — Nebraska Natural Resource Districts established and widespread nitrate testing begins. 1974 — Safe Drinking Water Act adopts 10 mg/L nitrate-N maximum contaminant level. | 1970s | Nebraska irrigated corn: 110 bu/ac; 1.6 lb N/bu; 2.5 million acres; about 10% irrigated by pivot 1979 — Inorganic N fertilizer identified as main nitrate source in Central Platte. First NRD irrigation water allocations. |
| 1981 — UNL Extension Nitrate Task Force. 1984 — First adverse birth outcomes research. 1985 — Nebraska Natural Resources Commission study identifies growing regions impacted. Groundwater Foundation established. 1988 — Children’s Groundwater Festivals begin. | 1980s | Nebraska irrigated corn: 125 bu/ac; 1.3 lb N/bu; 5 million acres; about a third irrigated with center pivots. 1985 — Groundwater Management & Protection Act. 1987 — Central Platte NRD first quality policies. 1989 — Bazile Triangle established in northeast Nebraska. |
| 1991 — Nitrate travel timing and amount estimated. 1993 — Public Water Supplies required to provide drinking water below 10mg/L nitrate-N. Creighton builds first reverse osmosis filtration. 1996 — CDC Report on miscarriages from nitrate. | 1990s | Nebraska irrigated corn: 145 bu/ac; 1.2 lb N/bu; 0.15 inches water/bu; 5 million acres 1992 — On-Farm Research program started. 1994 - UNL Corn Nitrogen calculator first created. 1993 — Crop nitrogen sensors recommended. 1999 — Nitrate leaving corn rootzone 24-42 mg/L. |
| 2004 — International workgroup review of nitrate and health (updated 2018). | 2000s | Nebraska irrigated corn: 165 bu/ac; 71% pivot; 1.0 lb N/bu; 0.14" water/bu; 4.8 million acres 2005 — Renewable Fuel Standard for ethanol. |
| 2010 — International Agency for Research on Cancer determines nitrate is probably carcinogenic. 2013 — More than 1 out of 3 Nebraska irrigated acres have groundwater exceeding 10 mg/L. | 2010s | Nebraska irrigated corn: 190 bu/ac; 86% pivot; 0.8 lb N/bu; 0.13" water/bu; 5.3 million acres 2015 — Project SENSE, sensor-based N. 2017 — UNL TAPS competition for N & irrigation. |
| 2023 — Nitrate shown to release uranium. EPA reopens evaluation of chronic health effects. | 2020s | Nebraska irrigated corn: 205 bu/ac; 91% pivot; 0.8 lb N/bu 2023 — nitrate leaving corn rootzone 17-22 mg/L. |
