May 11, 2007

|
|
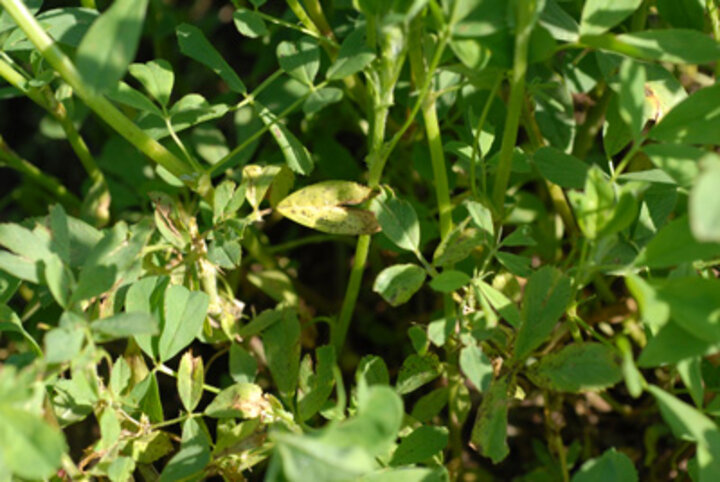
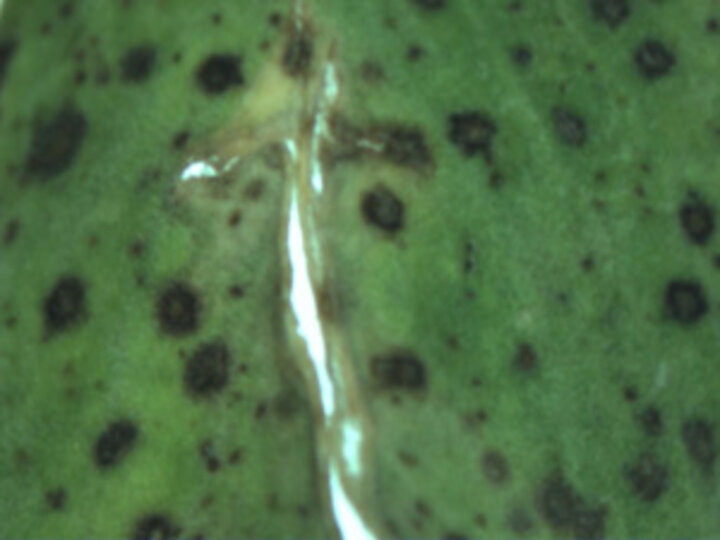
| Figure 1. Dark brown to black spots on the lower leaves of alfalfa indicative of spring black stem and leaf spot. (Photos by Stephen Wegulo and Julie Breathnach) | |
|
Figure 2. Lesions caused by spring black stem and leaf spot as seen under a dissecting microscope. |

|
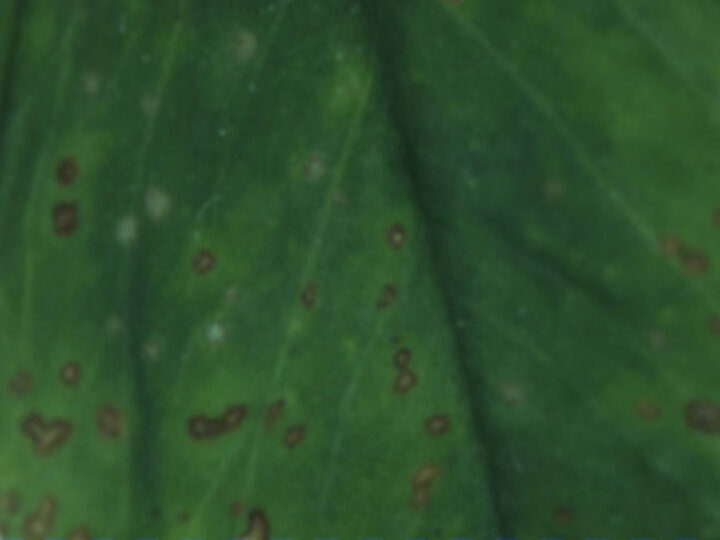
Figure 3. Lesions caused by Leptosphaerulina leaf spot as seen under a dissecting microscope. |
Numerous alfalfa fields, especially in south central and southeast Nebraska, are severely infected with multiple fungal leaf diseases. The two most prevalent diseases are spring blackstem and leptosphaerulina leaf spot; common leaf spot also occurs but much less frequently.
In most severely affected fields, many leaves are likely to be lost prior to harvest due to these diseases and little can be done to prevent it. This problem adds to the losses experienced in these same fields from the severe freezing temperatures of early April.
Many fields look very ragged with uneven regrowth. Fields often look somewhat yellowish or a dull green and appear to be deteriorating. Closer examination of the leaves reveals numerous small, brown to black spots, especially on lower leaves (Figure 1), indicative of spring black stem and leaf spot. The small spots caused by spring black stem and leaf spot are often referred to as tar spots. These can increase in size and coalesce (Figure 2). Later stages start blackening the stem and cause leaves to yellow and fall.
Leptosphaerulina leaf spot is more common on newer leaves near the top of the plant. It forms small lesions with tannish centers and brown or reddish-brown borders, often surrounded by a yellowish chlorotic area (Figure 3).
Fields tend to be worst in areas that recently received heavy rains. Both diseases are initiated by spores released from fruiting structures formed on leaves and stems during the previous year. During rainy weather in the spring, the fruiting structures release spores which are spread by splashing water and wind. It is likely that the recent rain aggressively caused the release and spread of spores, causing rapid and heavy infections. Moist or humid conditions will cause further spread of the diseases.
Likely not insects
Many growers are mistakenly attributing the deterioration of these fields to insects like alfalfa weevil or potato leafhopper. Some insects often are present but the number of insects present is too low to merit use of insecticides in most diseased fields, especially the widespread applications that are occurring.
Treatment Options Limited
Few fungicides are labeled for use on alfalfa. Kocide is the fungicide most commonly used, but it will not reduce the damage already present on the alfalfa. It will not help the current crop, but could reduce infection of regrowth following harvest. However, it is unlikely to be cost effective.
Harvest Recommendations
Deciding when to harvest these ragged, uneven and diseased fields is a more difficult question. Growth won't return to normal until after harvest. Usually an early harvest is recommended to salvage leaves before they die and drop to the ground. An early harvest might turn things around quickly; however, it also could weaken already weak plants even more. Some may even die. The best strategy may be to wait another 10 days until plants have had seven weeks to recover from the freeze, then harvest no matter how ugly the forage. In many fields, much of the bottom stem may have no attached leaves due to diseases. After harvest, expect regrowth to be a bit slow.
Bruce Anderson
Extension Forage Specialist
Stephen Wegulo
Extension Plant Pathologist
