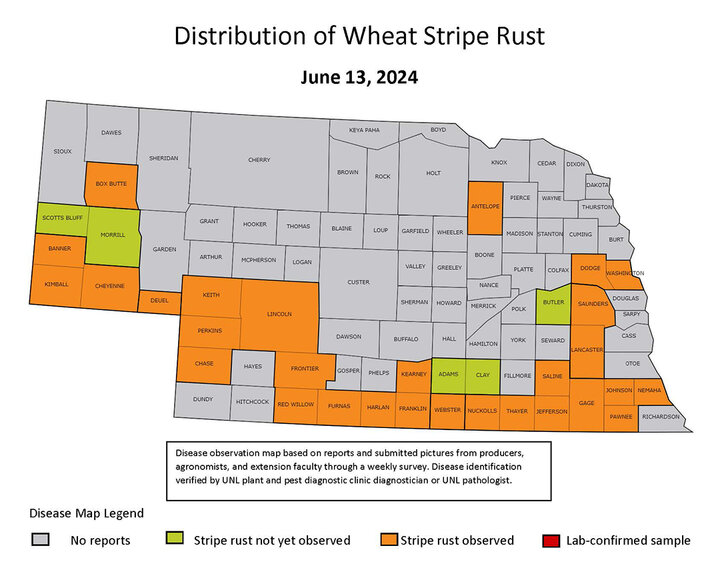
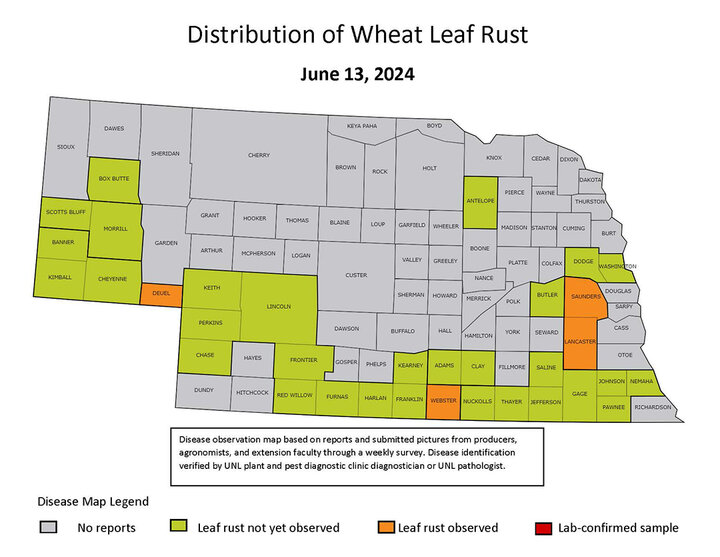
This week’s disease surveys were conducted concurrently with annual wheat field days (Figure 1). The predominant disease in wheat fields is stripe rust (Figure 2). Leaf rust (Figure 3) was first observed in late May at trace levels.
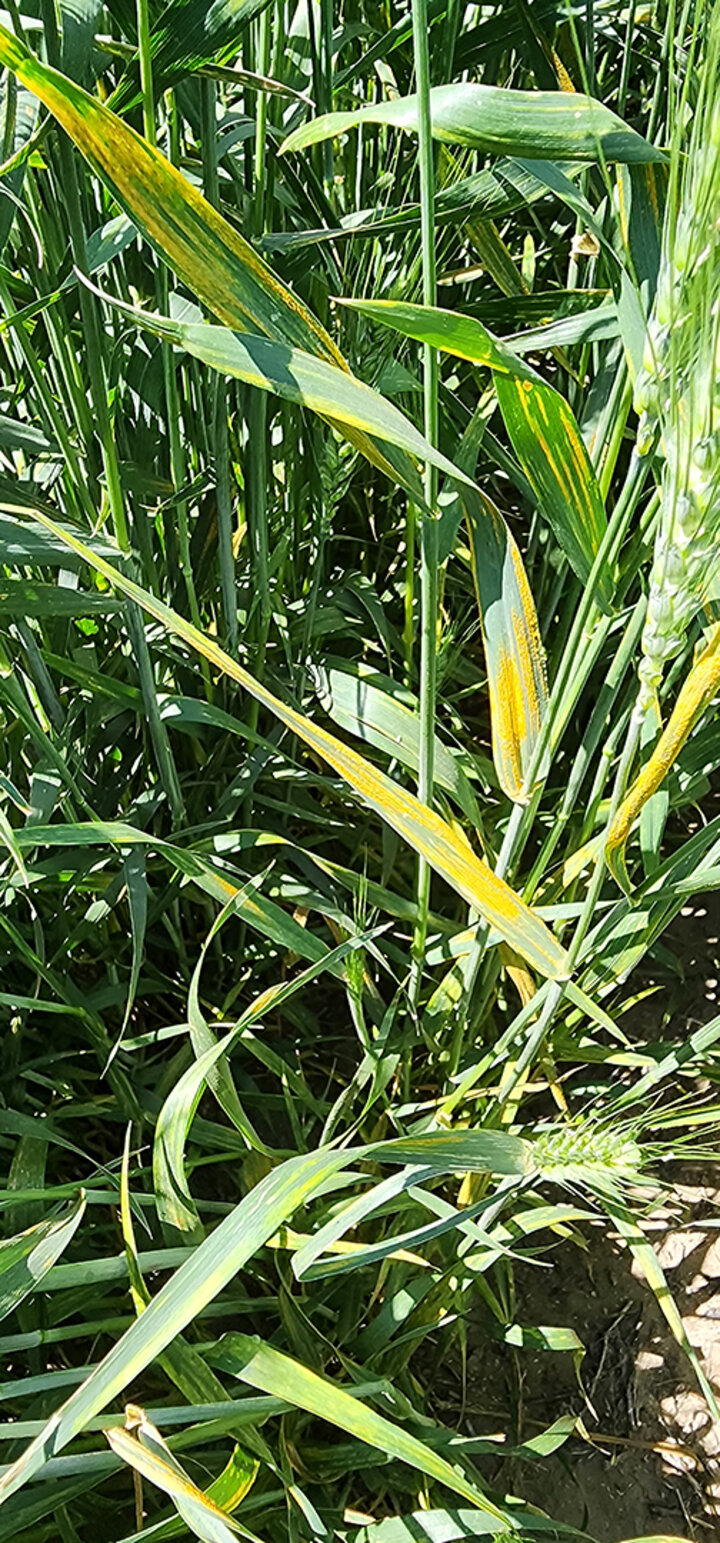


Stripe rust is present in all wheat-growing regions in Nebraska (Figure 4). Leaf rust has been observed in four counties (Figure 5).
Bacterial leaf streak (Figure 6) is present in some fields, but only at trace levels.
Other diseases observed this week are the fungal leaf spots (Septoria tritici blotch and tan spot) and trace levels of the wheat streak mosaic virus disease complex.

Management
It is too late in the growing season to apply a fungicide to control stripe rust and other fungal diseases. Leaf rust arrived late and is not expected to significantly impact yield. Stripe rust, leaf rust and fungal leaf spots are managed by planting resistant varieties and applying a fungicide timed to protect the flag leaf.
There are no chemical or biological products that are effective in controlling bacterial leaf streak. To minimize its occurrence, plant certified seed. The wheat streak mosaic virus disease complex is managed by planting resistant or tolerant varieties and by controlling volunteer wheat and grassy weeds before planting in the fall. The volunteer wheat and grassy weeds should be completely dead at least two weeks before planting.

