The end of the field season is near and many producers are likely to spend some time watching the yield monitor as they harvest. This time is a great opportunity to identify spots in the field with unexplained yield loss.
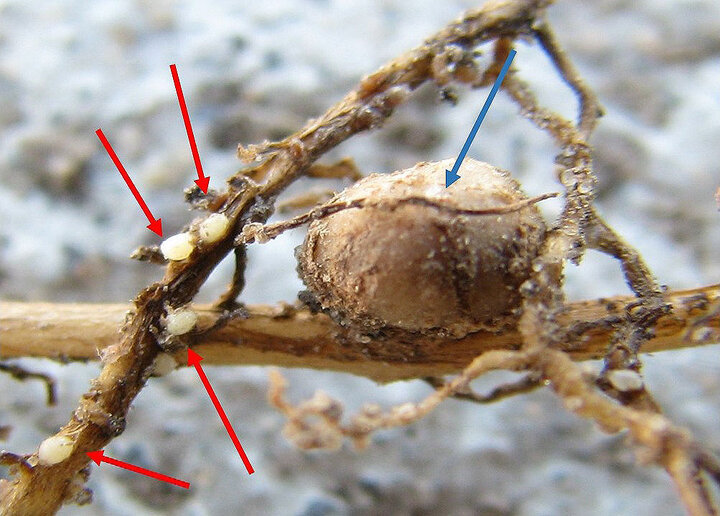
A potential explanation for these areas could be soybean cyst nematode (SCN) (Figures 1 and 2). This pest is the number one yield limiting biotic agent of soybeans in North America and is estimated to cause U.S. producers $1.5 billion a year. The reason this pest is so insidious is because SCN can cause up to 30% yield loss with no significant above-ground symptoms. For this reason, SCN is an invisible threat that many producers do not know they have and are not actively managing it in their fields.
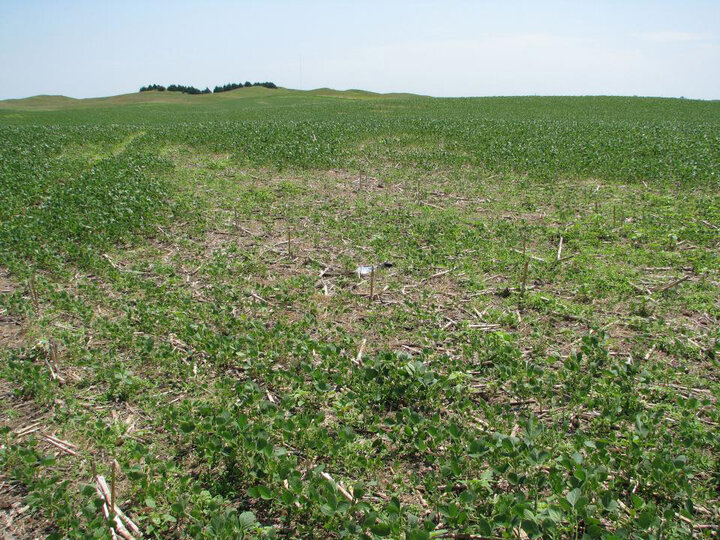

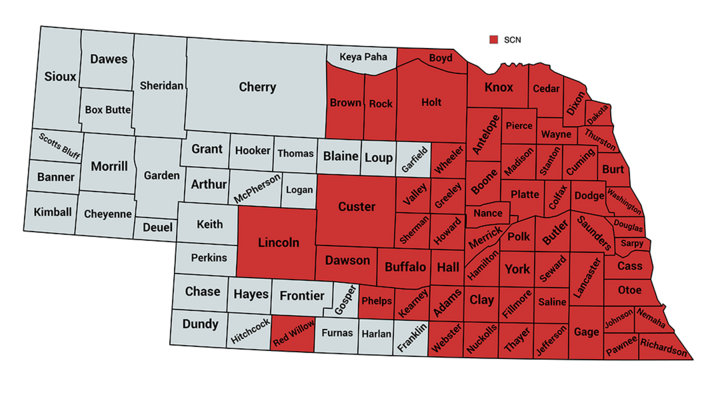
As of March 15, 2024, SCN has been identified in 60 Nebraska counties (Figure 3). Fortunately, effective management options are available, but the first step in deciding to manage is to determine if the nematodes are present in your field. The best time to test fields for SCN is at the end of a soybean season. This is when SCN levels will be at their highest in the soil.
Currently, the Nebraska Soybean Board is sponsoring soybean cyst nematode sample analysis for samples from any Nebraska field. To take advantage of this program, contact your local extension office or the UNL Applied Soybean Pathology Lab for free soil sampling bags and submit soil samples using the following procedure.
Sampling Procedure
Collect SCN samples with a one-inch diameter soil sampling probe or spade. Collect at least 15 to 20 soil cores in a zigzag pattern from across the field. Samples should be collected from the root zone at a depth of about six to eight inches across about 10 to 20 acres. Break up the collected soil cores and mix them well in a bucket. Place at least two cups of the composite soil sample in a bag and submit for SCN testing. A sealable plastic bag works great to prevent samples from drying, or use marked SCN sample bags available at your local Nebraska Extension office or the UNL Plant & Pest Diagnostic Clinic.
While sampling, keep in mind that anything that can move soil can move soybean cyst nematode. For this reason, there are several areas with increased SCN introduction risk. Below is a list of high-risk areas that you should consider sampling.
- Areas of the field where soybean crops yielded less than expected.
- Areas of the field where soybean plants appeared stunted, yellow and/or defoliated earlier than the rest of the field.
- Low spots in fields.
- Previously flooded areas of fields.
- Field entryways.
- Along field borders.
- Areas where sudden death syndrome (SDS) or brown stem rot (BSR) developed.
Submit samples to:
UNL Plant & Pest Diagnostic Clinic
448 Plant Sciences Hall
P.O. Box 830722
Lincoln, NE 68583-0722
Sample bag information to include:
- Name
- Address
- Email address
- Phone number
- Field name or ID for your reference
- Number of acres the sample represents
- Crop history of the field
- This year’s crop
Management
Once you have identified fields with SCN, there are four broad management recommendations. The first is to rotate between resistant varieties. There are several resistance sources available. The most common are “PI88788” and “Peking”. Effort should be made to rotate between resistance sources if possible as SCN populations are evolving to overcome the PI88788 resistance source. Rotation will help prolong the life expectancy of current resistance sources while new resistance is being developed.
The second management recommendation is to rotate to a non-host crop. Fortunately, corn, wheat and alfalfa are non-hosts that work well with common Nebraska rotation. While rotation alone will not get rid of SCN, it will help decrease the number of SCN in the soil.
The third management recommendation is to consider the use of a nematode-protectant seed treatment. There are many new seed protectant products entering the market. If you plan to use one, be aware that these should only be used in combination with a resistant soybean variety. A seed treatment should not be considered a replacement for a resistant variety for any pathogen, including SCN.
The final recommendation is to continue to monitor SCN populations and levels through testing. As you make management changes, monitoring of SCN levels is important to determine if your management is effective. Sampling should be continued every two to three years to ensure management is effective. This will also provide another opportunity to monitor uninfected fields.
Many producers are experiencing some yield loss to SCN. Actively managing these populations will provide the opportunity to recover this yield. Remember that this pest is often invisible and soil testing is the only way to accurately identify and monitor the pest. If you don’t recall the last time you tested, it is time to test again. Pick up sample bags for free testing from your local extension office.
More Information
- Please contact us in Nebraska Extension for more information.
- The SCN Coalition
- Crop Protection Network – Soybean Cyst Nematode of Soybean
- CropWatch Soybean Cyst Nematode Information

