Due to the USDA Risk Management Agency (RMA) recently allowing “cover crops” to be grazed or mechanically harvested after September 1, mechanical harvest of cover crops will be allowed for contracts approved for the 2019 Cover Crops for Disaster Assistance Initiative. Cover crops cannot be harvested for grain. This week the Nebraska NRCS office announced a third cutoff date for applications to provide cost-share assistance for producers to plant cover crops on prevented planting acres. The application deadline for the 2019 Cover Crops for Disaster Assistance Initiative funded through EQIP has been extended to July 19. Contact your local NRCS office for more information.
Using Cover Crops to Protect and Improve Prevented Planting Fields
Farmers unable to plant in a timely manner due to flood damage need to weigh not only their program and insurance options (“prevented planting”), but also their agronomic options to protect and improve the soil and ensure long-term productivity.
The NRCS Nebraska Agronomy Technical Note 112 explains some of the advantages of growing cover crops in prevented planting acres, building versus losing nitrogen, herbicide issues, and recommended planting dates in Nebraska for various cover crop species.
See the April 2019 NRCS Cover Crop Agronomy Guide.
Additional information on prevented or delayed planting is available in CropWatch:
and on the USDA Farmers.gov website:
Producers planting cover crops on prevented planting acres are not required to follow the Natural Resources Conservation Services Cover Crop (340) conservation practice standard and specifications for the county, nor does the chosen plant species have to be listed on the NRCS conservation practice standard. Farmers may obtain advice from any source listed in the Good Farming Practices Handbook regarding selection of and planting requirements for the cover crop.
NRCS does not need to be involved with farmers wanting to plant a cover crop to meet the requirements of this crop insurance option. However, NRCS employees can assist farmers and that assistance must conform to the appropriate NRCS practice standard and agency technical assistance policy. (RMA, the Farm Services Agency (FSA), and NRCS agreed to this in a meeting on June 25, 2019.)
Following are guidelines for using cover crops to qualify for disaster assistance from NRCS through EQIP. Before selecting a cover crop, check plant-back restrictions listed on the label of any previously applied herbicides. For more information, see Check Herbicide Restrictions before Planting and Using Cover Crops.
Timing and Harvest
- Cover crops must be allowed to grow for at least six to eight weeks prior to grazing or mechanical harvest.
- Mechanical harvest must leave at least 6 inches of stubble to provide some cover over winter.
Recommendations for Using Corn as a Cover Crop
Corn is considered a cover crop species in Nebraska, either as part of a mix or in a monoculture, although a monoculture of corn would normally be discouraged.
- The new seeding rates for corn, as used in NE-CPA-7, have been updated to:
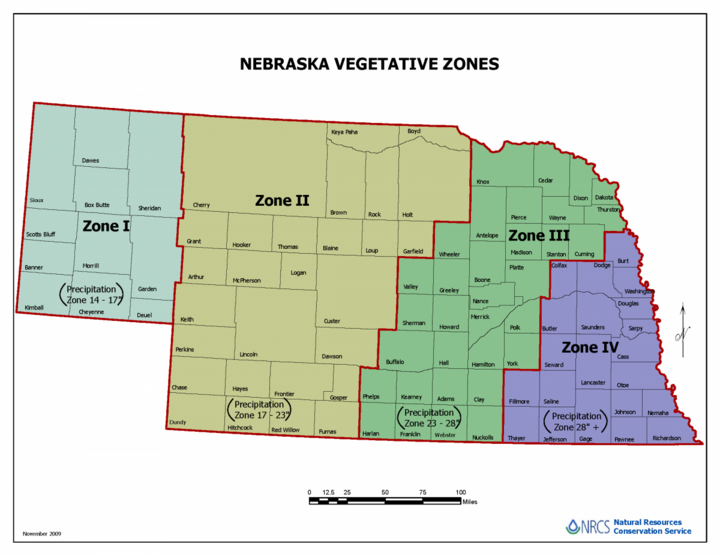
- Vegetative Zone I – 12 lbs/acre
- Vegetative Zone II – 18 lbs/acre
- Vegetative Zone III – 24 lbs/acre
- Vegetative Zone IV – 30 lbs/acre
- The use of BMR grazing corn is recommended if it’s to be grazed as a cover crop. Conventional corn is allowed if it’s to be harvested for silage.
- Bin run seed is allowed, providing growers use their own seed. Buying or selling bin run seed would be a violation of Nebraska law regarding the sale of seed. In addition, growers need to be sure they are not violating any patent or labeling restrictions associated with GMO seed.
- To minimize weed competition, cover crops must be planted on 15-inch or narrower rows.
- Broadcast seeding is not recommended for corn or other large-seeded cover crop species.
- It is strongly recommended that growers:
- consider planting at least two additional species with corn that will continue to grow after harvest of silage or
- consider seeding a second cover crop after harvest, especially on highly erodible land (HEL).
- If additional species are planted with corn, the seeding rate for corn can be reduced accordingly as long as the total seeding rate for all species is 100% or more.
- Use of a starter fertilizer and perhaps some additional nitrogen (30-50 lbs) may be necessary to ensure the establishment and vigor of the cover crop.

