- Japanese beetles are gradually becoming a pest of corn and soybean in Nebraska. While they are not yet a significant problem in northeast Nebraska, we expect numbers to increase in the coming years. The beetles defoliate soybeans, and clip silks in corn. If silk clipping occurs to fresh silks, kernel development may be affected. In Nebraska, we have a Japanese beetle look-a-like, the sand chafer. Sand chafer adults are not a problem in Nebraska crops, so it is important to learn the difference between these two beetles.
- Painted lady and other caterpillar species are common defoliators in Nebraska soybeans. They make up a complex of defoliators that may require management, but occasionally a single species reaches economically damaging levels. Caterpillar populations are typically regulated by disease; however, if environmental conditions are right, the populations can increase significantly. Besides the painted lady caterpillar, some of the most common caterpillars we see in Nebraska are loopers, green clover worm, yellow woolybear, and silverspotted skipper.
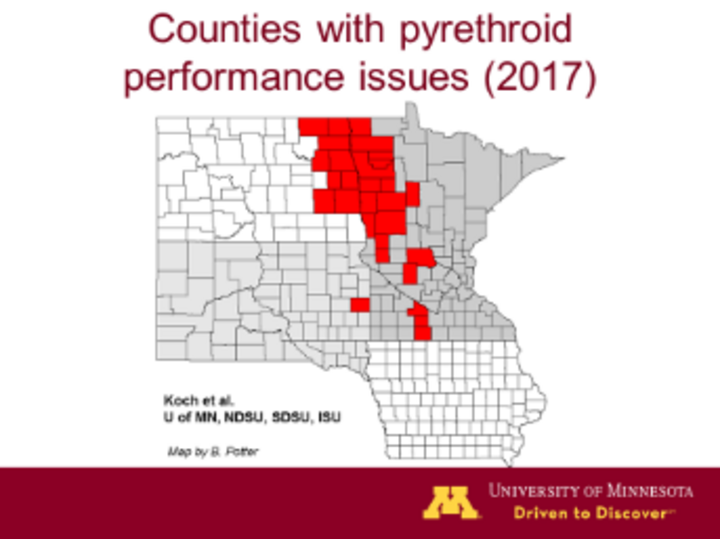
- There have been reports in Minnesota and surrounding areas of less than expected control of soybean aphids by pyrethroids, and in a few cases chlorpyrifos. Two pyrethroids that have shown significantly less than expected mortality in bioassays are λ-cyhalothrin and bifenthrin. While no confirmed insecticide resistance has been reported in Nebraska, growers should monitor their fields after insecticide treatment because many of our summer migrants likely come from southwest Minnesota and northwest Iowa.
Resources for Additional Information
- Managing Soybean Defoliators, NebGuide G2259
- Soybean Aphid Management in Nebraska, NebGuide G2063;
- Soybean Aphid Speed Scouting, Extension Circular 1582 or apps for Apple devices (http://itunes.apple.com/us/app/aphid-speed-scout/id454600279?mt=8) or Android devices (https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=edu.unl.aphidspeedscout).
There are numerous species of insect pests in Nebraska crops, some new and some reoccurring. The best way to reduce the injury of these pests is:
- Regularly scout your fields.
- Use management guidelines recommended by Nebraska Extension.
- Keep abreast of current Nebraska agricultural issues in CropWatch.