Land application of organic materials for soil management in Nebraska is important for several reasons:
- Nebraska has about 1100 beef feedlots finishing a total of 5 million head per year.
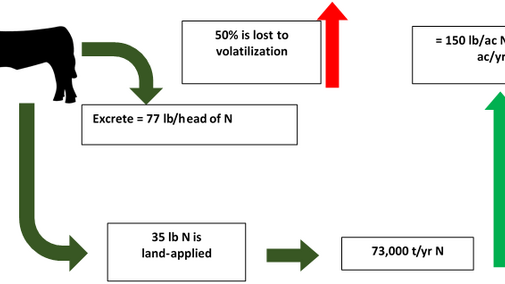
- Beef manure N applied annually is equal to 150 lb/ac N applied to about 1.2 million acres (Figure 1).
- Other land-applied livestock manure, municipal wastes, and other organic materials contribute additional N for crop production.
- The availability of applied organic N and the fertilizer N substitution values of applied organic materials is not well predicted, although guidelines exist (Table 1).
- The uncertainty of applied organic N availability leads to over-application of fertilizer N, resulting in low N use efficiency of applied N.
- Organic N release varies with properties of the organic material, including the C:N ratio and cellulose and lignin content, with weather and soil conditions, and with management.
| Table 1. Current recommendation of estimated first-season availability (%) of manure organic-N. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| % organic-N available in first year1 | |||
| Source | Solid | Fresh liquid | Stored liquid |
| Beef/dairy | 25% | - | 35% |
| Poultry | 30% | - | - |
| Swine | - | 50% | 35% |
| Compost | 15%2 | ||
1 Assumes spring-seeded crops; for fall-seeded crops, multiply values by 70% to account for delayed mineralization during cooler months. |
|||
Research is underway to improve the prediction of the fertilizer N substitution values for organic materials.
- Eight organic materials of diverse properties are being evaluated at eight locations for three years under both irrigated and rainfed conditions. Treatments were applied in 2016.
- One material, Novozyme, is a by-product resulting from an enzyme production process. The bacteria are killed by adding CaO. The by-product is composed of CaCO3 and denatured microbial biomass with a low organic C to organic N ratio (C:N) and low lignin and cellulose content (low acid detergent fiber (ADF); Table 2).
- The feedlot manures have the highest C:N but low ADF.
- The municipal biosolid products have relatively high lignin and cellulose content (ADF).
- Organic N applied varied with expected mineralization rate from 215 to 680 lb/acre; the sensor readings indicated that the amount available to the crop was similar for all organic materials.
- Each location has an N ramp, i.e. a series of N levels with no organic material applied for determination of N response functions.
- No fertilizer N was applied pre-plant for the organic material treatments, but N was applied in-season at V14 in 2016 and at V12 in 2017 according to NDRE canopy sensor guidance.
- The apparent recovery of organic material N (AONR) and fertilizer N replacement (FNR) for each organic material were calculated by relating the yield for each organic material receiving in-season N application to the N ramp for determining the fertilizer equivalent rate of N.
Research Findings
The apparent recovery of organic N (AONR) and fertilizer N replacement (FNR) (Table 2) from the applied organic materials in eastern Nebraska were:
- similar for rainfed and irrigated;
- 77% greater for a loamy sand compared with silt loam and silty clay loam soils;
- not affected by C:N ratio for these materials, but likely to be less if C:N is much higher;
- 2.34 and 2.29 times more, respectively, for livestock manures compared with municipal biosolid products; and
- not reduced by composting compared to not composting.
Compared with previous estimates of FNR (Tables 1, 2):
- FNR was 28% higher for cattle manure.
- FNR was 67% higher for compost.
| Organic material | C:N | ADF | AONR | FNR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stockpiled feedlot manure | 10.3 | 226 | 0.27 | 0.32 |
| Feedlot scraping | 11.8 | 205 | 0.25 | 0.29 |
| Turkey manure | 9.5 | 211 | 0.28 | 0.33 |
| Dairy manure compost | 8.7 | 285 | 0.3 | 0.34 |
| Novozyme bio-product | 6 | 84 | 0.24 | 0.28 |
| Lincoln municipal biosolid | 7.1 | 387 | 0.13 | 0.15 |
| Fremont biosolid composted | 9.7 | 440 | 0.13 | 0.15 |
| Fremont biosolid dewatered | 8.3 | 378 | 0.1 | 0.11 |
Research is continuing and it is too early to draw conclusions. Results from 2017, the second crop after application, will also be reported at the Crop Production Clinics.